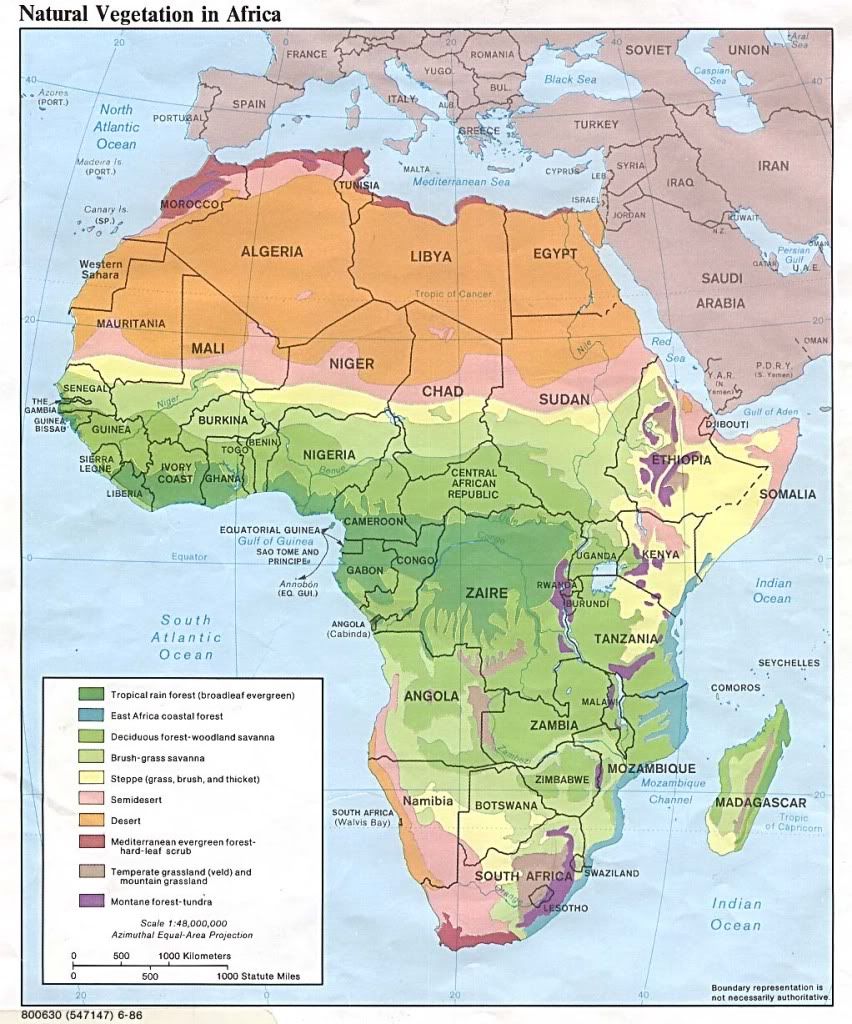
The African Savanna biome is a tropical grassland in Africa between latitude 15° North and 30 degrees S and longitude 15 degrees W and 40° West. It covers Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Cote D'ivore, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Botswana, and South Africa.
Annual rainfall in the African Savanna is about the same as that of Wisconsin. During the rainy season, beginning in May and ending in November, they get fifteen to twenty-five inches of rain a month. In the dry season they only get about four inches of rain. The dry season occurs more then seven months of the year, from October to March in the southern hemisphere and April to September in the northern hemisphere. The dry season comes in the low sun period and the wet season comes in the high sun period. They have a wet-dry tropical climate.
A rolling grassland dotted with trees is one way to define the African Savanna. The African Savanna is a thornbush savanna, which has many different kinds of plants such as acacia Senegal, candelabra tree, jackalberry tree, umbrella thorn acacia, whistling thorn, Bermuda grass, baobabs, and elephant grass. The Serengeti Plains are a grass savanna that has very dry but nutrient-rich volcanic sand. Around 2 million large plant-eating mammals live in the savanna. There are 45 species of mammals, almost 500 species of birds, and 55 species of acacia in the Serengeti Plains. There are animals such as lions, African wildcats, klipspringer, steenbok, Burchell's zebra, African Savanna monitor, and puff adders. They have the largest diversity of hoofed animals in the world including antelopes, wildebeest, buffalos, zebras, and rhinoceros.










 , and I believe the african savannahs have to be considered very
, and I believe the african savannahs have to be considered very