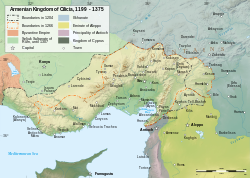
Cilician Armenia 1199-1375, Etchmiadzin Cathedral, Roman Temple, Armenia at its greatest extent under Tigranes the Great (95-66 BC)
© 1993-2003 Microsoft Corporation. ENCARTA, All rights reserved.
The historic region of western Asia Armenia, which in ancient times was an independent country comprising the southern Caucasia and northeastern Asia Minor. The region is a complex of plateaus traversed by mountain ranges; the highest point being, Mount Ararat at 16,945 ft. It is drained by the headstreams of the Euphrates, Tigris, and Aras rivers; the principal lakes are Van, Urmia, and Sevan. Armenia has a climate that varies between the subtropical and subtemperate. Sections of the region, especially the river valleys, are highly arable and contain rich vineyards and orchards. The high tablelands are chiefly pastoral. Armenia contains a variety of mineral deposits.
Ethnologically Armenians are classified as Caucasoid, and linguistically as Indo-European. According to some authorities, their ancestors include the aboriginal people of the region; the Chaldeans, who occupied it late in the 2nd millennium BC; and later invaders. The valley of the Araxes (now Aras) River and the plateau around Van Gölü (Lake Van) was a dominion, from about 1270 to 850 BC, of a kingdom, sometimes called Van, but known in nearby Assyria as Urartu (Hebrew Ararat). The name Armenia first appeared in the Behistun inscription of Darius I, king of Persia about 521 BC. In 612 BC, Armenia was conquered by Media, which ruled it until 549.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Armenia
Recent archeological studies have found the earliest leather shoe, skirt, and wine-producing facility in Armenia, dated to about 4000 B.C. This points to an advanced early civilization In the Bronze Age; several states flourished in the area of Greater Armenia, including the Hittite Empire (at the height of its power), Mitanni (South-Western historical Armenia), and Hayasa-Azzi (1500–1200 BC). The Nairi people (12th to 9th centuries BC) and the Kingdom of Urartu (1000–600 BC) successivel established their sovereignty over the Armenian Highland. Each of the aforementioned nations and tribes participated in the ethnogenesis of the Armenian people. Around 600 BC, the Kingdom of Armenia was established under the Orontid Dynasty. The kingdom reached its height between 95 and 66 BC under Tigranes the Great, becoming one of the most powerful kingdoms of its time within the region.
Historically Armenia was practiced a Mazdean branch of Zoroastrianism, focused on the worship of Mihr (the Avestan Mithra). Christianity spread into the country as early as AD 40. King Tiridates III (AD 238–314) made Christianity the state religion in AD 301, becoming the first officially Christian state, ten years before the Roman Empire. After the fall of the Armenian kingdom in AD 428, most of Armenia was incorporated as a marzpanate within the Sassanid Empire. Following an Armenian rebellion in AD 451, Christian Armenians maintained their religious freedom, while Armenia gained autonomy.
© 1993-2003 Microsoft Corporation. ENCARTA, All rights reserved.
As a center of Christianity, Armenia opposed the Zoroastrian Persians after the 4th century. The conquest of Persia by the Arabs in 642 was followed by their overlordship in Armenia. In 653, however, the Arab caliph chose an Armenian prince to administer the country, designating him patrician of Armenia. In time the patricians became virtual kings, and in 886 the Bagratuni dynasty reestablished the Armenian kingdom, and ruled the country during the 9th and 10th centuries. Many churches and vast irrigation works survive from that era.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Armenia
Between 428–636, Armenia emerged as the Emirate of Armenia, an autonomous principality within the Arabic Empire, reuniting Armenian
lands previously taken by the Byzantine Empire as well. The principality was ruled by the Prince of Armenia, recognised by the Caliph and the Byzantine Emperor. It was part of the administrative division/emirate Arminiyya created by the Arabs, which also included parts of Georgia and Caucasian Albania. The Principality of Armenia lasted until 884, when it regained its independence from the weakened Arabic Empire.The re-emergent Armenian kingdom was ruled by the Bagratuni dynasty, and lasted until 1045. In time, several areas of the Bagratid Armenia separated as independent kingdoms and principalities such as the Kingdom of Vaspurakan ruled by the House of Artsruni, while still recognizing the supremacy of the Bagratid kings. The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, 1199-1375.
In 1045, the Byzantine Empire conquered Bagratid Armenia. Soon, the other Armenian states fell under Byzantine control as well. The Byzantine rule was short lived, as in 1071 Seljuk Turks defeated the Byzantines and conquered Armenia at the Battle of Manzikert, establishing the Seljuk Empire. To escape death or servitude at the hands of those who had assassinated his relative, Gagik II, King of Ani, an Armenian named Roupen went with some of his countrymen into the gorges of the Taurus Mountains and then into Tarsus of Cilicia. The Byzantine governor of the palace gave them shelter where the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia was eventually established.
© 1993-2003 Microsoft Corporation. ENCARTA, All rights reserved.
About 1240 Armenia was invaded by the Mongols, who ruled it until the early 15th century. A period of confusion, during which Iran for a short time controlled Armenia, ended when the Ottomans conquered most of the region in the 16th century. Thereafter it suffered ceaseless warfare between the Ottoman Empire and Iran.
St Geogory Patron Saint of Armenia, Topography, 7th AD Khor Virap monastery in the shadow of Mount Ararat, Trad. Armenian dance