How much human brain can we add to a rats brain and do experiments on it?
Miniature human-brain-like structures transplanted into rats can send signals and respond to environmental cues picked up by the rats’ whiskers, according to a study. This demonstration that neurons grown from human stem cells can interface with nerve cells in live rodents could lead to a way to test therapies for human brain disorders.
Scientists would like to use brain organoids — tiny brain-like structures grown from human stem cells — to study neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders that humans develop. But the organoids mimic human brains only so far. They don’t develop blood vessels and so can’t receive nutrients, meaning that they don’t thrive for long. And they don’t get the stimulation they need to grow fully: in a human infant’s brain, neurons’ growth and how they develop connections with other neurons are based in part on input from the senses.
To give brain organoids this stimulation and support, neuroscientist Sergiu Pasca at Stanford University in California and his colleagues grew the structures from human stem cells and then injected them into the brains of newborn rat pups, with the expectation that the human cells would grow along with the rats’ own cells. The team placed the organoids in a brain region called the somatosensory cortex, which receives signals from the rats’ whiskers and other sensory organs and then passes them along to other brain regions that interpret the signals.
Human brain cells mature much more slowly than rat cells, so the researchers had to wait for more than six months for the organoids to become fully integrated into the rat brains. But when they examined the animals’ brains at the end of that time, they saw that the integration had been so successful that it was almost like adding “another transistor to a circuit”, Pasca said at a 10 October press conference.
Some of the challenges are ethical. People are concerned that creating rodent–human hybrids could harm the animals, or create animals with human-like brains. Last year, a panel organized by the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine released a report concluding that human brain organoids are still too primitive to become conscious, attain human-like intelligence or acquire other abilities that might require legal regulation. Pasca says that his team’s organoid transplants didn’t cause problems such as seizures or memory deficits in the rats, and didn’t seem to change the animals’ behaviour significantly.
But Arlotta, a member of the National Academies panel, says that problems could arise as science advances. “We can’t just discuss it once and let it be,” she says. She adds that concerns about human organoids need to be weighed against the needs of people with neurological and psychiatric disorders. Brain organoids and human–animal hybrid brains could reveal the mechanisms underlying these illnesses, and allow researchers to test therapies for conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. “I think we have a responsibility as a society to do everything we can,” Arlotta says.
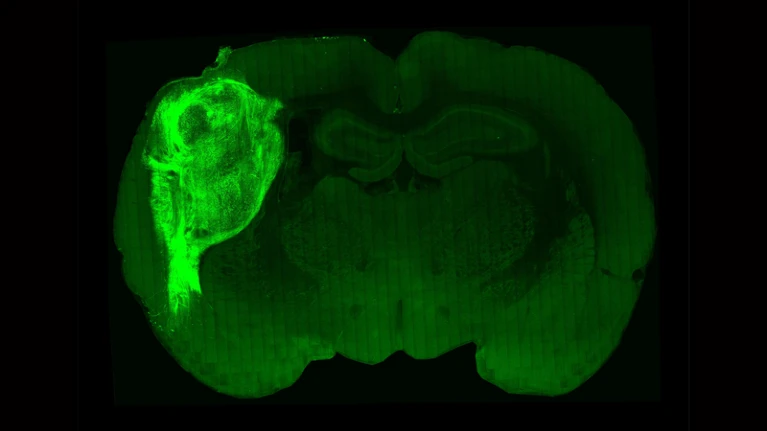
Researchers have transplanted a human brain organoid (bright green) into the brain of a newborn rat pup, creating a hybrid brain in which the neurons interface.
Miniature human-brain-like structures transplanted into rats can send signals and respond to environmental cues picked up by the rats’ whiskers, according to a study. This demonstration that neurons grown from human stem cells can interface with nerve cells in live rodents could lead to a way to test therapies for human brain disorders.
Scientists would like to use brain organoids — tiny brain-like structures grown from human stem cells — to study neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders that humans develop. But the organoids mimic human brains only so far. They don’t develop blood vessels and so can’t receive nutrients, meaning that they don’t thrive for long. And they don’t get the stimulation they need to grow fully: in a human infant’s brain, neurons’ growth and how they develop connections with other neurons are based in part on input from the senses.
To give brain organoids this stimulation and support, neuroscientist Sergiu Pasca at Stanford University in California and his colleagues grew the structures from human stem cells and then injected them into the brains of newborn rat pups, with the expectation that the human cells would grow along with the rats’ own cells. The team placed the organoids in a brain region called the somatosensory cortex, which receives signals from the rats’ whiskers and other sensory organs and then passes them along to other brain regions that interpret the signals.
Human brain cells mature much more slowly than rat cells, so the researchers had to wait for more than six months for the organoids to become fully integrated into the rat brains. But when they examined the animals’ brains at the end of that time, they saw that the integration had been so successful that it was almost like adding “another transistor to a circuit”, Pasca said at a 10 October press conference.
Some of the challenges are ethical. People are concerned that creating rodent–human hybrids could harm the animals, or create animals with human-like brains. Last year, a panel organized by the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine released a report concluding that human brain organoids are still too primitive to become conscious, attain human-like intelligence or acquire other abilities that might require legal regulation. Pasca says that his team’s organoid transplants didn’t cause problems such as seizures or memory deficits in the rats, and didn’t seem to change the animals’ behaviour significantly.
But Arlotta, a member of the National Academies panel, says that problems could arise as science advances. “We can’t just discuss it once and let it be,” she says. She adds that concerns about human organoids need to be weighed against the needs of people with neurological and psychiatric disorders. Brain organoids and human–animal hybrid brains could reveal the mechanisms underlying these illnesses, and allow researchers to test therapies for conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. “I think we have a responsibility as a society to do everything we can,” Arlotta says.

Researchers have transplanted a human brain organoid (bright green) into the brain of a newborn rat pup, creating a hybrid brain in which the neurons interface.






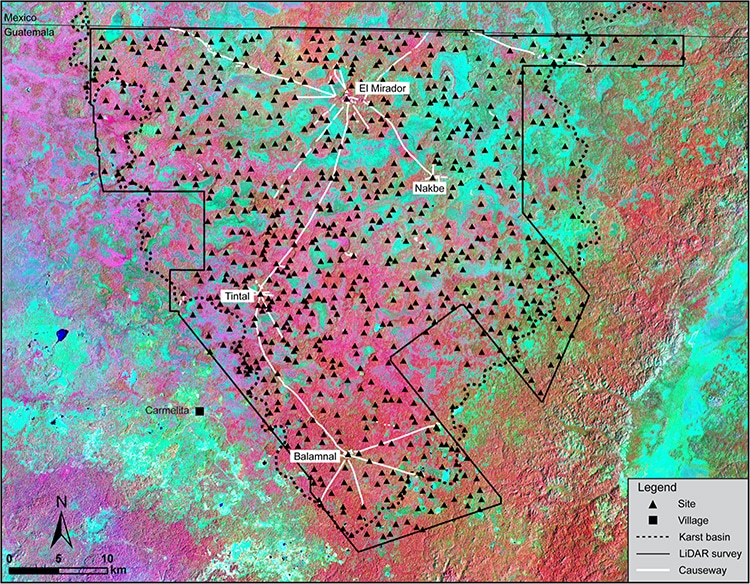
 The road between El Mirador and La Tintal is approx. 20 km/12½ miles.
The road between El Mirador and La Tintal is approx. 20 km/12½ miles.